Biogas Reduces Costs and Increases Efficiency By Converting Waste to Energy
In the United States alone, millions of tons of organic waste are produced each year. Organic waste includes things like manure from agriculture, sludge filtered from sewage water, municipal solid waste, food waste, crop residues, and more.
According to the Environmental and Energy Study Institute, organic wastes, when not properly managed, pose a significant risk to public and environmental health. During decomposition, organic wastes generate large amounts of methane, a powerful greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions and the risk of pollution to waterways, organic waste can be removed and used to produce biogas, a renewable source of energy.
Biogas and Biogas Systems
Biogases, such as methane, are gaseous fuels that are produced during the fermentation of organic matter. Biogas systems use a natural, biological anaerobic digestion process to recycle organic waste, turning it into energy in the form of gas, and valuable soil products in the form of liquid and solids. Biogas is typically made up of methane (50–75%), carbon dioxide (25–50%), and smaller amounts of nitrogen (2–8%). The precise percentages depend on a variety of factors, including retention time and ambient temperature.
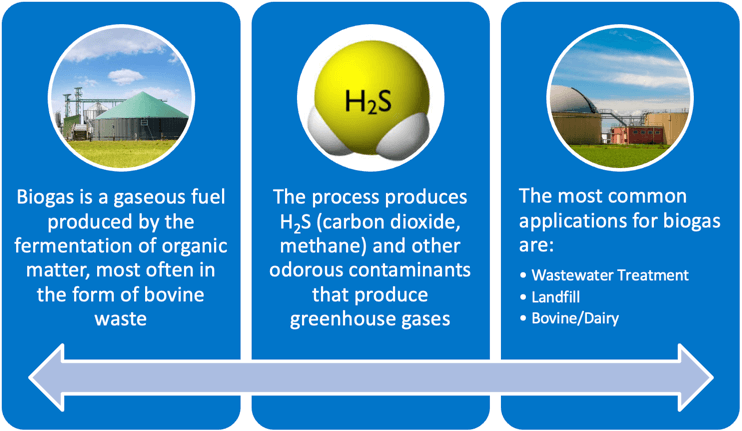
Biogas can be used in a variety of applications for the generation of heat and energy. The primary markets served by biogas systems include agriculture, landfill/food waste, and water resource recovery facilities. As a renewable energy option, biogas systems are both cost-effective and environmentally responsible.
The United States has more than 2,300 biogas production sites. The top U.S. producers of biogas include: California, Texas, North Carolina, Georgia, Iowa, Wisconsin, New York, Minnesota, Pennsylvania, and Arkansas. Currently there is vast potential for growth in the biogas industry, with 15,000 new sites ripe for development and ready to provide significant economic, environmental, and energy production benefits.
Biogas Desulphurization with Sulphasorb Fe™ Adsorbent Media
Biogas production for renewable energy requires the removal of H2S through a process called desulphurization. PureAir Filtration has developed Sulphasorb Fe™, a media that is ideally suited for biogas applications. Sulphasorb Fe™ is an iron oxide-based scavenger that breaks new ground in the removal of H2S due to its removal capacity that is minimum 25% by weight.
Competing iron oxide or iron hydroxide scavengers produce an elemental sulfur build up on the outside of the media. Sulphasorb Fe™ eliminates this problem, allowing the media to continue adsorbing. This innovative formula has been successfully used in applications up to 100,000 ppm.
Sulphasorb Fe™ Advantages
- Long lasting media life
- Cost-effective and consistent performance
- Effective in humid air
- Doesn’t require oxygen
- Oxygen extends media life
| Benefits | Features |
|---|---|
| Powerful |
|
| Low Maintenance |
|
| Specifications |
|
| Multiple Applications |
|
Compared to iron sponge technology, Sulphasorb Fe™ adsorbent media provides double the desulfurization capacity, creating a more cost-effective solution. The price combined with a rate of over 99% removal of H2S, makes Sulphasorb Fe™ an attractive solution for biogas applications.
To learn more about how PureAir Filtration can serve your biogas application needs, contact us today.


